When it comes to skincare, one product that often takes the backseat is sunscreen. Many people are unaware of the significance of sunscreen in their daily routine and the potential harm of exposing their skin without protection. If you are a sunscreen newbie, then don't worry! We’ve got you covered with this beginner sunscreen guide where we will explore why sunscreen is essential and the problems it helps to solve and by the end, you'll be well-prepared for sun safety all year round!
Table of contents
Do you really need a sunscreen? Do you know why dermatologists and skin experts emphasize the importance of sunscreen? Are you aware of the risks that sun radiation could cause? If not, then take a look below to understand the importance of sunscreen in your daily life.
The sun emits harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, namely UVA and UVB rays, which can penetrate the skin and cause damage. UVA rays are responsible for fast aging such as wrinkles and age spots, while UVB rays are the primary cause of sunburns. Continued exposure to these rays without proper protection can lead to long-term problems, including an increased risk of skin cancer.

Sunburn: When you spend too much time in the sun, your skin is exposed to UV radiation which can cause redness, pain, and in severe cases, blisters. Repeated sunburn can raise the risk of skin cancer.
Premature Aging: UV rays from the sun can break down collagen and elastin in your skin. This causes wrinkles, fine lines, and sagging, making your skin look older sooner. This is called photoaging.
Skin Cancer: Continued exposure to UV radiation can cause skin cancer. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, one in five Americans will develop skin cancer by the age of 70. Regular use of sunscreen can lower this risk a lot.
Hyperpigmentation: UV rays can also cause dark spots and uneven skin tone, often referred to as sunspots or age spots. They can be tough to treat and may stick around for a long time.
Eye Damage: UV radiation can hurt your eyes too, leading to problems such as cataracts and other eye diseases.
Example: Real-World Evidence: Truck Driver Study
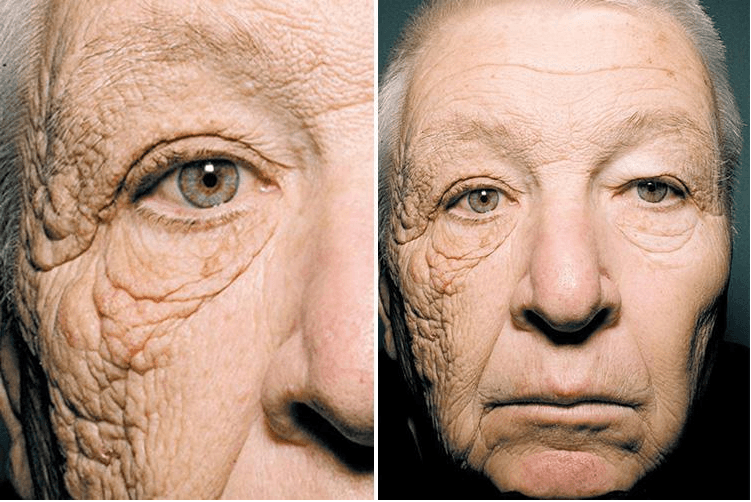
To show the long-term effects of UV exposure, here is an example from a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine. They studied the face of a truck driver who had spent 28 years driving with the left side of his face exposed to the sun through the window.
They found that the left side of the face which was exposed to the sunlight showed more damage than the right side. The left side had deep wrinkles, thickened skin and noticeable sagging which were all clear signs of photoaging.
This case showcases that how UV rays can cause serious damage over time and that it's so important to protect your skin, not just during outdoor activities but during your everyday activities where sun exposure is minimal. Hence, consistent use of sunscreen is essential to avoid these harmful risks.
Summry:
The sun's UV rays cause skin damage, leading to cancer, premature aging, sunburn, hyperpigmentation, and eye issues. A truck driver study highlights the severe, cumulative harm of daily sun exposure.
Ever wondered what extra cautions you can take to protect your skin beyond the sunscreen? There are various home and self-care practices that one can undertake to enhance our sun protection. By incorporating these easy tips into daily life, you can create a comprehensive defense against UV damage.
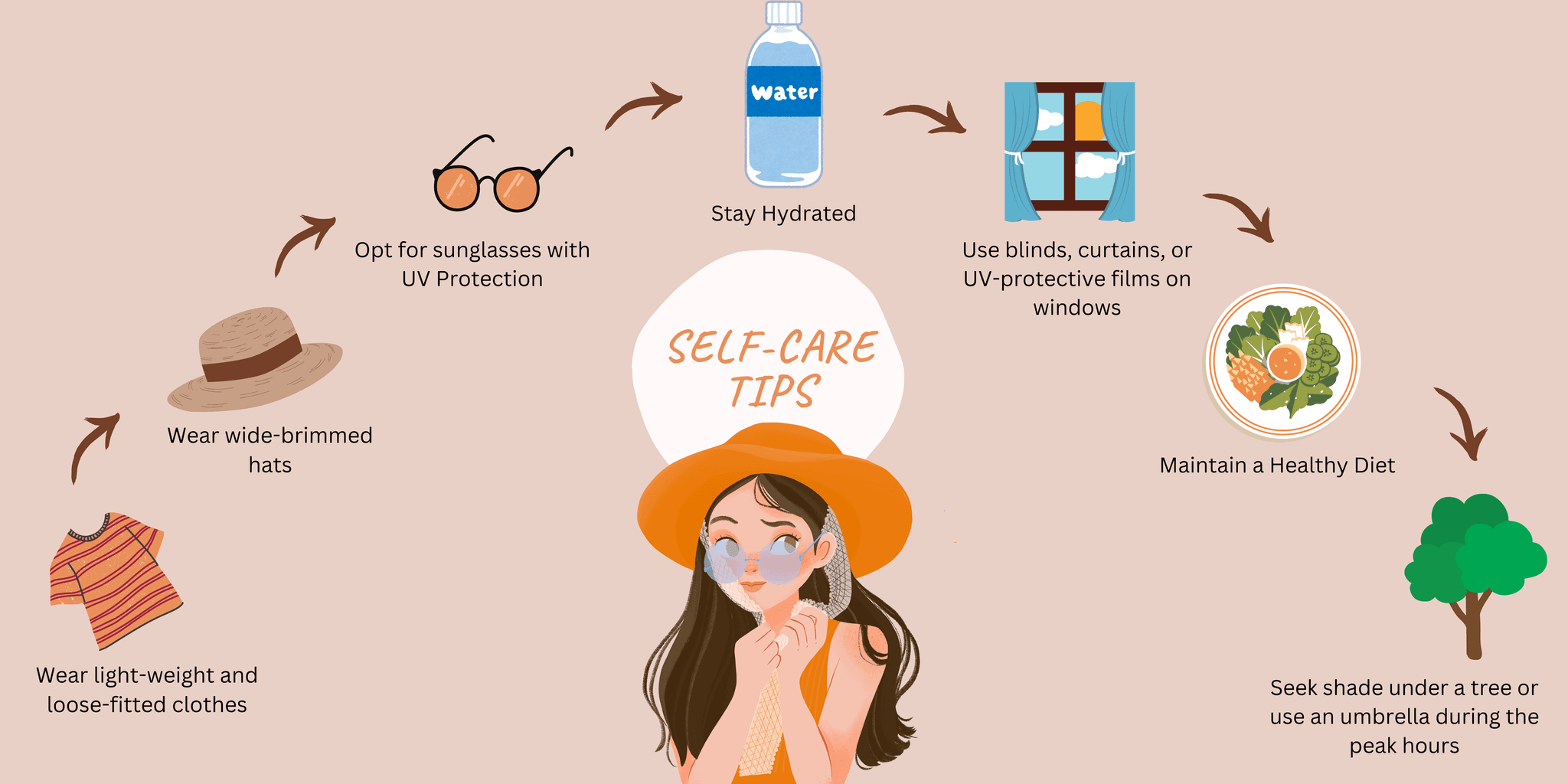
Wear Protective Clothing: Opt for lightweight, loose-fitting, and tightly woven fabrics that cover your arms, legs, and neck. Don’t forget to wear wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses with UV protection to protect your face and eyes.
Block UV rays Indoors: Make sure your home is equipped with blinds, curtains, or UV-protective films on windows. These measures will help to lower your overall sun exposure.
Hydrate to Radiate: Drink enough water to keep yourselves hydrated and maintain a healthy skin.
Plan smart outdoor activities: To minimize your exposure to UV rays and prevent sunburn, you can schedule your outdoor activities in early morning or in the late afternoon.
Beware of Reflective Surfaces: Surfaces like water, sand, and snow can reflect and intensify the sun’s rays. Always remember to take extra precautions by wearing protective clothing and applying adequate sunscreen frequently.
Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help protect your skin from sun damage. You can include berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and nuts into your diet to boost your skin’s natural defense against UV radiation.
Seek Shade: One of the simplest and most effective ways to protect yourself from the sun is to seek shade, especially during peak hours when the sun's rays are the strongest. Stay under a tree, umbrella, or any other form of shade to minimize direct exposure to the sun.
Check your skin regularly: Do a self-examination of your skin to detect any changes or abnormalities early on. Look for any new moles, changes in existing moles, or any other new or suspicious marks. Consult a dermatologist if you notice anything concerning.
Remember to follow these home and self-care practices. Make these habits a part of your daily life to keep your skin healthy and protected from the sun's harmful rays.
Summry:
Self care you can start right away are seek shade, wear protective clothing, use sun-protective accessories, install window coverings, stay hydrated, time outdoor activities, avoid reflective surfaces, eat healthy, and check skin regularly.
Are you often confused about the different types of sunscreen and which one is better for your skin? You've probably heard about physical and chemical sunscreens but aren’t sure what makes them different. Let’s understand it with the help of a visual.
There are two main types – chemical and physical.

Physical Sunscreen: It is also known as mineral sunscreen and it works by creating a barrier against your skin that reflects and scatters the UV rays away from your body. If you have sensitive or acne-prone skin then you can opt for this one as it contains ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide which are more gentle and causes less irritation. This sunscreen leaves a white residue when applied, usually known as white cast. Though newer improved versions are available in the market.
Chemical Sunscreen: It absorbs the UV rays and converts them into heat, which is then released from the body. It contains ingredients like oxybenzone, avobenzone, octisalate, and octocrylene which are suitable for oily skin. It is thinner and easier to apply and most importantly doesn’t leave a visible white layer while some individuals may experience skin reactions. The most important thing to consider is that you need to apply it 20 minutes before exposing yourself to the sun in order to be effective.
Both sunscreens are effective and provide you with maximum sun protection when used correctly. Choosing between them is a personal choice depending on your skin type, preferences and sensitivities. Always opt for a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 and the key to protection against UVA & UVB rays is reapplying it frequently.
Summry:
Physical sunscreens reflect UV rays, while chemical sunscreens absorb and convert them. Both sunscreens have their pros and cons, so consider your skin type and preferences to choose the best option for effective sun protection. Go for SPF 30+ and no matter what you choose, make sure you don't skip it!
Do you struggle to choose the right sunscreen texture according to your skin type? When it comes to choosing the right sunscreen texture, we usually focus on SPF and tend to forget about the importance of its texture. Let’s explore different types of textures so that you can choose the right one based on your preferences.

1. Gel Sunscreen: Gel sunscreens are water-based, lightweight sunscreens that can feel less oily when applied and are perfect for oily and acne-prone skin. They get easily absorbed into your skin and leave you with a refreshing feeling.
Stick Sunscreen: It comes in a solid stick format, making it convenient to apply on targeted areas like the face, lips and under the eyes. It is invisible and doesn’t leave a white residue.
Milk Sunscreen: Perfect for all skin types as it is lightweight and has a runny texture, which gets evenly distributed and absorbed into your skin quickly.
Spray Sunscreen: They come in liquid form that can be sprayed onto the skin, making it easier to cover large parts. Due to its light texture, it feels nearly non-existent so be sure to spray multiple layers for the best effect. This sunscreen is ideal for people who are constantly on the go.
Cream Sunscreen: It has a thick and creamy consistency that provides good coverage and hydration. It's a go-to for people with normal to dry skin and who enjoy a little extra hydration.
Powder Sunscreen: It comes in the form of loose powder and provides a lightweight and mattifying finish. It can be applied with a brush or sponge and is a great option to give touch-ups throughout the day.
7 Tinted Sunscreen: This sunscreen has a hint of colour that gives you light coverage for a natural and even complexion. Perfect for those who want to skip foundation.
Summry:
Gel for a lightweight feel, cream for extra hydration, milk for all skin types, spray for on-the-go application, tinted for natural coverage, stick for targeted protection, invisible for quick absorption, matte for a non-greasy finish, and powder for a mattifying effect. Stay protected and keep your skin healthy!
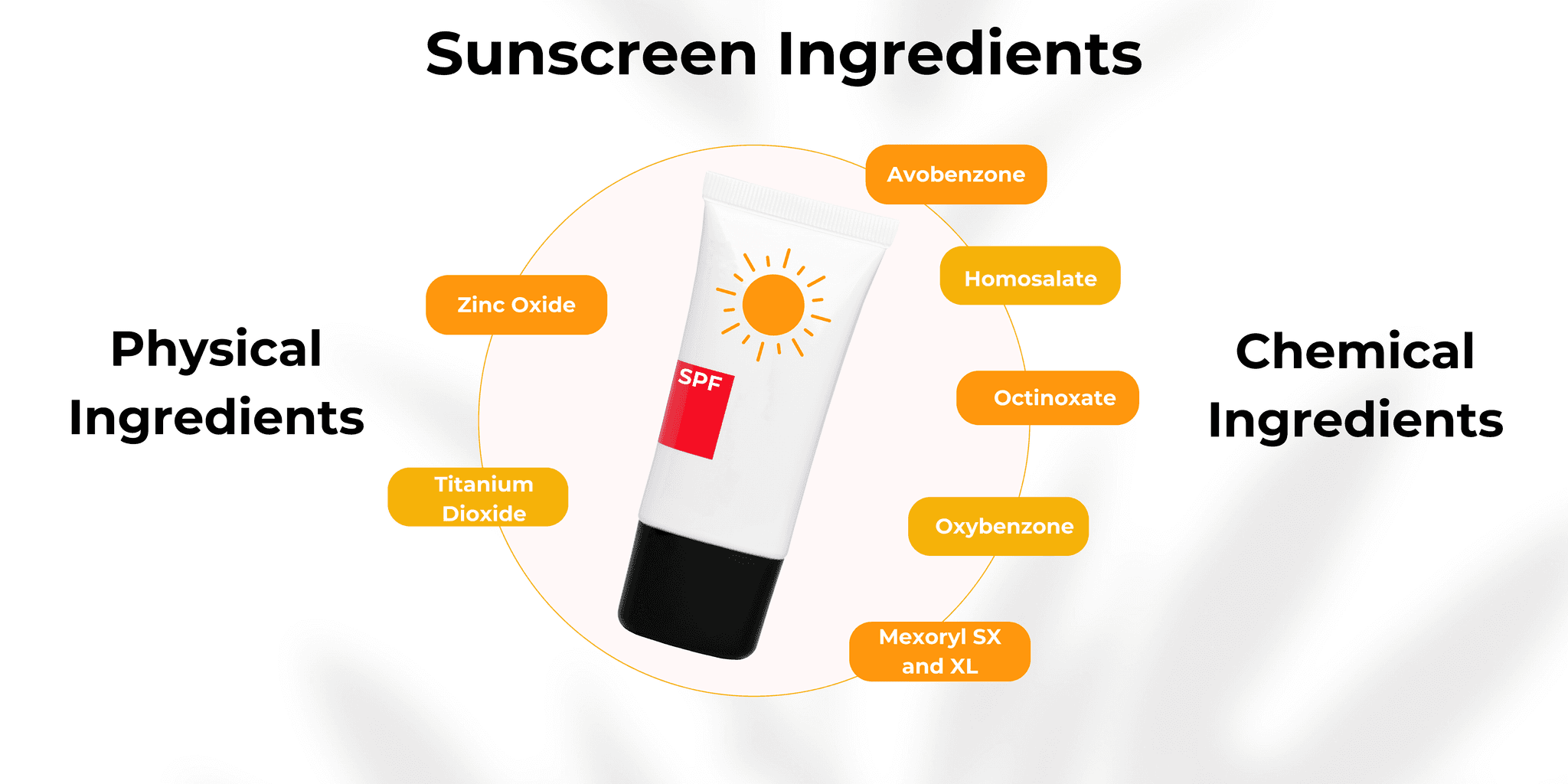
Did you ever notice the ingredients on a sunscreen bottle and ever wondered what those mean? When it comes to sunscreen, not all are equal. The magic lies in its ingredients. Here's a breakdown to make you understand the essential components that make your sunscreen a true skin savior.
1: Zinc Oxide: Also referred to as a "physical blocker," it sits on top of the skin and reflects UVA and UVB rays. It's gentle on sensitive skin, making it perfect for those with allergies or skin problems. Plus, it offers broad-spectrum protection.
Titanium Dioxide: Similar to zinc oxide, it is another physical blocker that provides broad-spectrum protection. It’s usually used in combination with zinc oxide to enhance sun-blocking capabilities. It has a lightweight texture that makes it a popular choice for daily sunscreens that won't leave your skin feeling greasy.
Avobenzone: It’s one of the most effective chemical ingredients for blocking UVA rays and is crucial for preventing long-term skin damage and aging. It gets absorbed into the skin, transforming UV light into harmless heat. However, avobenzone needs to be stabilized with other ingredients to remain effective in sunlight.
Homosalate: It is a chemical sunscreen agent that absorbs UVB radiation and is primarily responsible for sunburn. It works by converting UV rays into less harmful heat, protecting the skin from immediate sun damage.
Octinoxate: This is another UVB blocker that helps prevent sunburn. It's one of the oldest and most commonly used sunscreen ingredients, but it's worth noting that octinoxate has been examined for its potential impact on coral reefs, leading to its ban in some regions.
Oxybenzone: It is a powerful UVB and short-wave UVA absorber and is effective but also controversial. Concerns about its potential to cause skin allergies and its impact on marine life have led to increased demand for oxybenzone-free sunscreens.
7: Mexoryl SX and XL: These are patented sunscreen agents that offer long-lasting protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Mexoryl SX is water-soluble, while Mexoryl XL is oil-soluble, providing a comprehensive shield against sun damage.
Summry:
When you choose a sunscreen, it's very important that you look beyond the SPF number and consider the ingredients. Each element plays a vital role in protecting your skin from different types of UV damage. Keep in mind to opt for broad-spectrum sunscreens that combine these powerful ingredients to ensure you're fully shielded from the sun's harmful effects.
Whenever you talk about sunscreen, you’ll often hear the word SPF. But what does it actually mean? Let’s dive into details.
What is SPF? SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor and indicates how well the sunscreen can protect you from UVA and UVB radiation of the sun. UVA rays are responsible for skin damage and premature aging, on the other hand, UVB rays cause sunburns.
How does SPF Work?
The SPF number tells you how long you can stay in the sun without getting sunburned, compared to if you weren’t wearing any sunscreen. For instance, SPF 30 means you can theoretically stay in the sun 30 times longer without burning. Here’s a quick breakdown:

SPF 15: Blocks about 93% of UVB rays.
SPF 30: Blocks about 97% of UVB rays.
SPF 50: Blocks about 98% of UVB rays.
SPF 70: Blocks about 99% of UVB rays.
Remember higher the SPF number, higher the protection. Anything above SPF 30 is good to go!
Broad-Spectrum Protection
While SPF indicates protection against UVB rays, it's also crucial to protect against UVA rays which penetrate deeper into the skin and cause premature aging and skin cancer. Use sunscreens labeled as "broad-spectrum" to ensure they provide protection against both UVA and UVB rays.
Summry:
SPF is crucial for sun protection. Understanding and choosing the right SPF can significantly reduce your risk of sunburn and skin damage. Use sunscreen consistently and find a product that suits your lifestyle.
1. Wear It Every Day Daily application of sunscreen is essential, regardless of the weather. UV rays can penetrate through clouds and windows, so make sunscreen a part of your morning routine to protect your skin consistently.
2. Give Yourself Some Prep Time Apply sunscreen at least 15-30 minutes before going outside. This allows the sunscreen to fully absorb into your skin and become effective in providing protection against UV rays.
3. Apply Liberally to All Exposed Body Parts Don’t skimp on the amount. Use about one ounce (a shot glass full) for your entire body. Cover all exposed areas, including your face, neck, arms, and legs. Proper coverage ensures maximum protection.
4. Pat, Don’t Rub When applying sunscreen, gently pat it onto your skin rather than rubbing it in. This method helps ensure even distribution and better absorption without irritating the skin.
5. Reapply Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if you are swimming, sweating, or towel-drying. Sunscreen wears off over time and needs to be replenished to maintain effective protection.
6. Don’t Forget the Hands, Ears, and Neck These areas are often overlooked but are just as vulnerable to UV damage. Make sure to cover your hands, ears, neck, and any other exposed areas to avoid sunburn and skin damage.
7. Wash It Off Properly Before Bed At the end of the day, cleanse your skin thoroughly to remove all sunscreen. This helps prevent clogged pores and allows your skin to breathe and regenerate overnight.
Summry:
The "7 laws of sunscreen" emphasize daily use, regardless of weather. Apply it 15-30 minutes before sun exposure and use a generous amount for full coverage. Pat it on, don't rub. Reapply every two hours or after swimming. Don’t overlook hands, ears, and neck. At day's end, wash it off to avoid clogged pores.
Finding the right sunscreen can be an overwhelming task, especially when you don't know your skin type. Let’s help you to identify your skin type so that you can choose the right sunscreen.
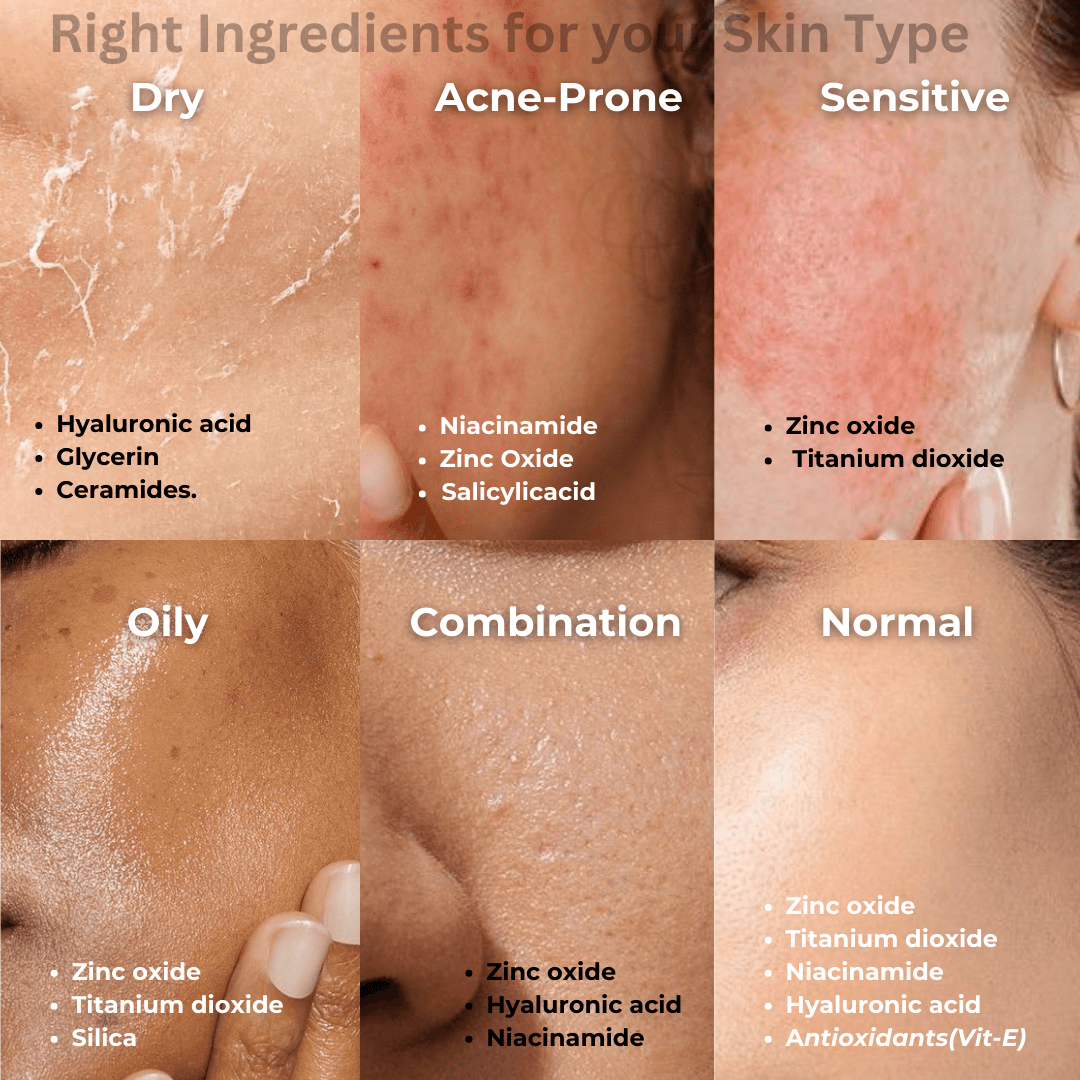
1. Dry Skin: If you have dry skin, cream sunscreens are your best friends because they provide the most hydration to your skin. Hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and ceramides are some ingredients to look for in a sunscreen as they will provide enough moisture to your skin!
Recommended Ingredients: Hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and ceramides.
Acne-Prone Skin: If you have acne-prone skin, avoid using products that can cause inflammation. Opt for gel sunscreens as they are lightweight and water-based in nature. Do check if they have soothing qualities, such as allantoin or panthenol, to help minimize irritation and outbreaks.
Recommended Ingredients: Niacinamide. zinc oxide, and salicylic acid.
Sensitive Skin: Similar to acne-prone skin. Thus, you should avoid any chemicals that can trigger your skin. Use lightweight sunscreens with soothing ingredients like cica, which is excellent for reducing inflammation and calming irritation.
Recommended Ingredients: Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide.
Oily Skin: Go for a gel sunscreen with a matte finish that is not comedogenic and acnegenic. Since oily skin has a shiny complexion, sunscreens with a matte finish can help reduce shine while also avoiding clogged pores and acne.
Recommended Ingredients: Zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, and silica.
Combination Skin: This skin type can be challenging to figure out which sunscreen will be best. There are versatile options like gel, cream, or milk sunscreens. So, choose the one according to your preference but ensure it contains ingredients that won't clog your pores. Look for something that offers your skin the right amount of hydration.
Recommended Ingredients: Zinc oxide, hyaluronic acid and niacinamide.
Normal Skin: Normal skin is relatively universal, so you can pretty much use any product you want. There's not much to worry about whether you want gel or cream as long as it works well on your skin, you're good to go!
Recommended Ingredients:Titanium Dioxide, zinc oxide, niacinamide, antioxidants(Vit-E) and hyaluronic Acid.
Summry:
For dry skin, use cream sunscreens with hyaluronic acid and glycerin. Acne-prone skin should choose lightweight gel sunscreens with niacinamide and zinc oxide. Sensitive skin benefits from physical sunscreens with cica and zinc oxide. Oily skin needs matte gel sunscreens with zinc oxide and silica. Combination skin can use versatile options, avoiding pore-clogging ingredients. Normal skin can use any compatible sunscreen.
1. What SPF Should I Choose? Question: How much SPF do I need for everyday use versus outdoor activities? Answer: For everyday use, SPF 30 is typically sufficient. For extended outdoor activities, opt for SPF 50 or higher. SPF 30 blocks about 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 blocks about 98% (Outlook India).
2. What’s the Difference Between Chemical and Physical Sunscreens? Question: Should I use a chemical or physical sunscreen? Answer: Chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, while physical sunscreens (like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide) sit on top of the skin and reflect UV rays. Choose physical sunscreens for sensitive skin and chemical sunscreens for a lightweight feel (Outlook India) (Ultimate Lists).
3. Is Broad-Spectrum Important? Question: Why is broad-spectrum protection necessary? Answer: Broad-spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays can age the skin and cause long-term damage, while UVB rays cause sunburn. Ensuring broad-spectrum protection helps prevent both types of damage (In-Cosmetics Connect).
4. How Often Should I Reapply Sunscreen? Question: How frequently do I need to reapply sunscreen? Answer: Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours, or more frequently if swimming, sweating, or towel-drying. This maintains its effectiveness throughout the day (Ultimate Lists).
5. Can I Use Sunscreen on My Face and Body? Question: Do I need separate sunscreens for my face and body? Answer: While you can use the same sunscreen for both, facial sunscreens are often formulated to be lighter and less greasy, making them more suitable for daily wear under makeup. Body sunscreens may be thicker and more hydrating (Outlook India).
6. Is Sunscreen Necessary Indoors or on Cloudy Days? Question: Do I need to wear sunscreen indoors or when it's cloudy? Answer: Yes, UV rays can penetrate windows and clouds. Wearing sunscreen indoors and on cloudy days helps protect your skin from cumulative damage (Outlook India).
7. Are Expensive Sunscreens Better? Question: Is it worth spending more on expensive sunscreens? Answer: Not necessarily. While higher-priced sunscreens may offer additional skincare benefits or more pleasant formulations, there are many affordable options that provide excellent protection. Focus on ingredients and SPF rather than price alone (Outlook India).
8. What Ingredients Should I Avoid? Question: Are there any ingredients I should avoid in sunscreens? Answer: Avoid sunscreens with oxybenzone and octinoxate if you are concerned about reef safety and potential skin irritation. Some people may also need to avoid fragrances and parabens if they have sensitive skin (In-Cosmetics Connect).
9. How Much Sunscreen Should I Apply? Question: How much sunscreen is enough? Answer: Use about one ounce (a shot glass full) to cover your entire body. For the face alone, a nickel-sized dollop is usually enough. Ensuring adequate application is key to effective protection (Outlook India).
10. Can I Use Sunscreen With Other Skincare Products? Question: Can I apply sunscreen over or under makeup and other skincare products? Answer: Yes, sunscreen should be the last step in your skincare routine before makeup. Apply it after your moisturizer and before your foundation. Some sunscreens are designed to work well under makeup without pilling (Ultimate Lists).
In conclusion, understanding and choosing the right sunscreen doesn't have to be complicated. By identifying your skin type, learning about different sunscreen types and textures, and knowing what ingredients to look for, you can select a sunscreen that perfectly fits your needs. Remember, sun protection is not just about sunscreen but also about incorporating overall healthy practices such as a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing stress, and getting enough sleep. By combining the right sunscreen with a holistic approach to health, you'll be well on your way to maintaining healthy, protected, and radiant skin. 🌟